By investing in Mutual Funds, an investor can earn returns in the form of capital gains and dividend** income, which are taxable in the hands of the investor.
- A capital gain / loss arises when an investor sells any number of units of Mutual Funds
- An investor receives a dividend in proportion to the number of units held at the time of announcement of dividend, which is distributed by companies to investors when they earn a surplus.
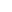
Tax on Capital Gains Received from Mutual Funds:
The tax on capital gains depends on the period of holding (short-term or long-term) and the type of capital asset.
- In the case of Equity Mutual Funds, an investment tenure of less than 1 year (12 months) is a short-term investment. Any investment of over one year is a long-term investment
- In case of Debt and Hybrid Mutual Funds, an investment tenure of up to 2 years (24 months) is a short-term investment and any investment of over 2 years (24 months) is considered as long-term.
Equity Mutual Funds / Equity Index Fund / Equity ETF / Equity FoF /
BAF / Equity Savings / Arbitrage / Aggressive Hybrid* |
Redemption up to Jul 22, 2024 (Pre-Budget) |
Redemption on or after Jul 23, 2024 (Post-Budget) |
| STCG |
LTCG |
STCG |
LTCG |
| Period of Holdings (Months) |
<12 |
>12 |
<12 |
>12 |
| Type of Gain |
Short-Term |
Long-Term |
Short-Term |
Long-Term |
| Taxation Rate |
15% |
10% (on gains above ₹1 lakh) |
20% |
12.50% (on gains above ₹1.25 lakh) |
*STT is applicable on these funds as >= 65% is invested in domestic equity shares BAF is considered here as in most cases BAF schemes maintain gross exposure of % or more to equity and equity related instruments.
| Debt Oriented Fund |
Investment prior to Apr 1, 2023 & redemption up to Jul 22, 2024 (Pre-Budget) |
Investment prior to Apr 1, 2023 & redemption on or after Jul 23, 2024 (Post-Budget) |
| STCG |
LTCG |
STCG |
LTCG |
| Period of Holdings (Months) |
<36 |
>36 |
<24 |
>24 |
| Type of Gain |
Short-Term |
Long-Term |
Short-Term |
Long-Term |
| Rate of Tax |
As per slab rate |
<20>% with indexation |
As per slab rate |
<12.50>% with no indexation |
| Debt Oriented Fund |
Investment after <Apr 1, 2023> & redemption up to <Jul 22, 2024> (Pre-Budget) |
Investment after <Apr 1, 2023> & redemption on or after <Jul 23, 2024> (Post-Budget) |
| STCG |
LTCG |
STCG |
LTCG |
| Period of Holdings (Months) |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
| Type of Gain |
Short-Term |
NA |
Short-Term |
NA |
| Rate of Tax |
As per slab rate |
NA |
As per slab rate |
NA |
| Gold ETFs /Silver ETFs / FoF / Multi-Asset Allocation, International FoFs, Hybrid Mutual Fund with <= 35% Investment in equity Instruments |
Investment prior to Apr 1, 2023 & redemption after Jul 23, 2024 |
Investment after Apr 1, 2023 & redemption after Jul 23, 2024 (till Mar 31, 2025) |
Investment after Apr 1, 2023 & redemption on or after Apr 01, 2025 |
| STCG |
LTCG |
STCG |
LTCG |
STCG |
LTCG |
| Period of Holdings |
<12 |
>12 |
NA |
NA |
<12 |
>12 |
| Type of Gain |
Short-term |
Long-term |
Short-term |
NA |
Short-term |
Long-term |
| Rate of Tax |
As per slab rate |
12.50% |
As per slab rate |
NA |
As per slab rate |
12.50% |
Debt Oriented Fund (>= 65% in SEBI Regulated Debt and Money Market Instruments)
Key abbreviations:
(STCG – Short Term Capital Gains, LTCG – Long Term Capital Gains, ETF – Exchange Traded Fund, FoF – Fund of Funds, BAF – Balanced Advantage Fund, STT – Securities Transaction Tax)
**Tax on Dividend Income received from Mutual Funds:
- From Apr 1, 2020, Mutual Fund dividends are taxable in the hands of investors. The dividend income is taxable under the head ‘income from other sources’ at the applicable income tax slab rate for the financial year
- Income Distribution-cum-Capital Withdrawal (IDCW) is a term used by Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to replace dividend option in Mutual Fund.
Disclaimer: The Union Budget 2024 has introduced significant changes to the taxation of Mutual Funds, aiming to simplify the tax structure and provide clarity for investors. These changes impact various types of Mutual Funds differently, altering how they are taxed over both the short and long term. Investors can learn how Mutual Funds are taxed if they are concerned that their returns from Mutual Funds will be reduced after paying taxes.